Markets
Which Countries Hold the Most U.S. Debt?
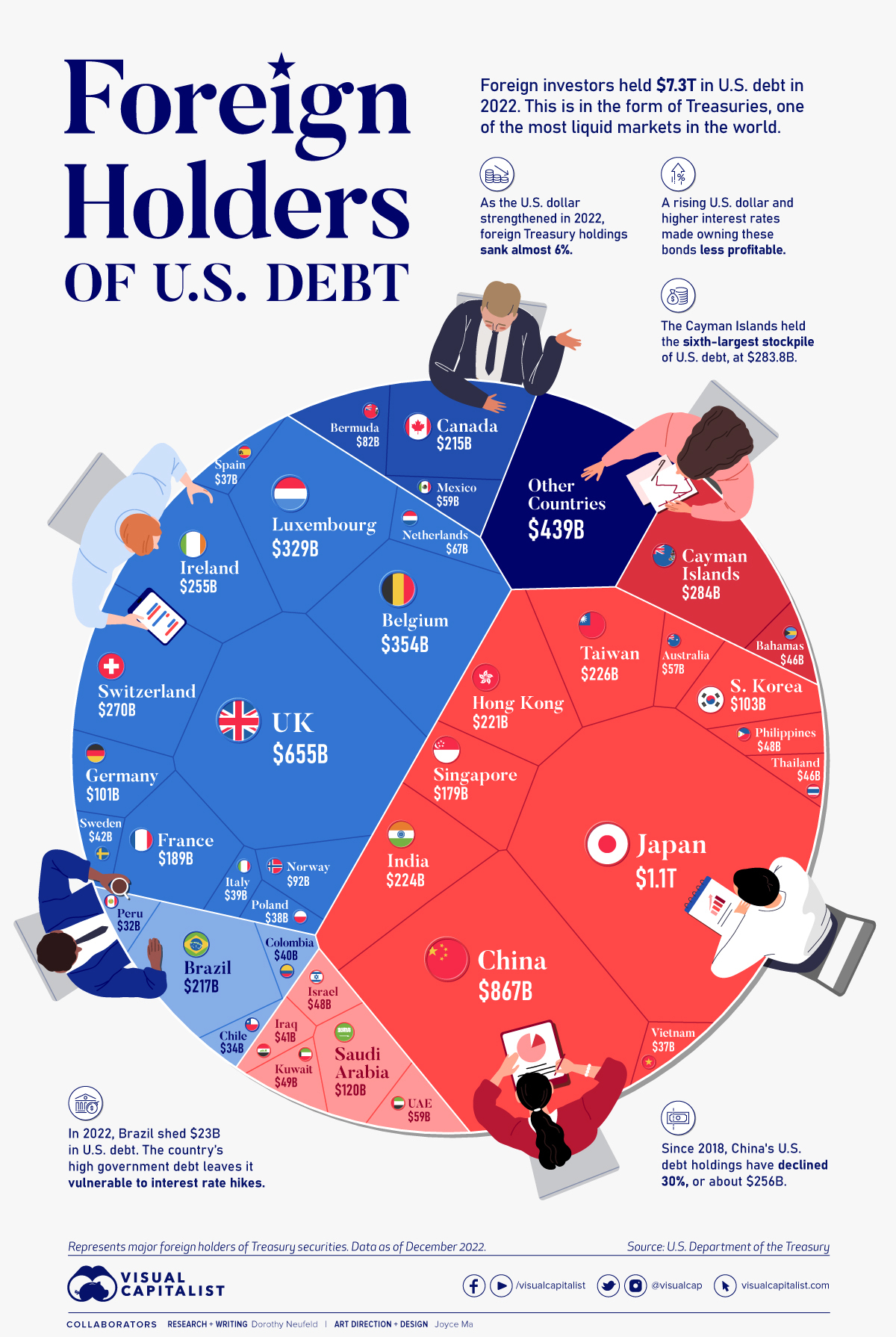
Which Countries Hold the Most U.S. Debt in 2022?
Today, America owes foreign investors of its national debt $7.3 trillion.
These are in the form of Treasury securities, some of the most liquid assets worldwide. Central banks use them for foreign exchange reserves and private investors flock to them during flights to safety thanks to their perceived low default risk.
Beyond these reasons, foreign investors may buy Treasuries as a store of value. They are often used as collateral during certain international trade transactions, or countries can use them to help manage exchange rate policy. For example, countries may buy Treasuries to protect their currency’s exchange rate from speculation.
In the above graphic, we show the foreign holders of the U.S. national debt using data from the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Top Foreign Holders of U.S. Debt
With $1.1 trillion in Treasury holdings, Japan is the largest foreign holder of U.S. debt.
Japan surpassed China as the top holder in 2019 as China shed over $250 billion, or 30% of its holdings in four years.
This bond offloading by China is the one way the country can manage the yuan’s exchange rate. This is because if it sells dollars, it can buy the yuan when the currency falls. At the same time, China doesn’t solely use the dollar to manage its currency—it now uses a basket of currencies.
Here are the countries that hold the most U.S. debt:
| Rank | Country | U.S. Treasury Holdings | Share of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇯🇵 Japan | $1,076B | 14.7% |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | $867B | 11.9% |
| 3 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | $655B | 8.9% |
| 4 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | $354B | 4.8% |
| 5 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | $329B | 4.5% |
| 6 | 🇰🇾 Cayman Islands | $284B | 3.9% |
| 7 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | $270B | 3.7% |
| 8 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | $255B | 3.5% |
| 9 | 🇹🇼 Taiwan | $226B | 3.1% |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 India | $224B | 3.1% |
| 11 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | $221B | 3.0% |
| 12 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | $217B | 3.0% |
| 13 | 🇨🇦 Canada | $215B | 2.9% |
| 14 | 🇫🇷 France | $189B | 2.6% |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | $179B | 2.4% |
| 16 | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | $120B | 1.6% |
| 17 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | $103B | 1.4% |
| 18 | 🇩🇪 Germany | $101B | 1.4% |
| 19 | 🇳🇴 Norway | $92B | 1.3% |
| 20 | 🇧🇲 Bermuda | $82B | 1.1% |
| 21 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | $67B | 0.9% |
| 22 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | $59B | 0.8% |
| 23 | 🇦🇪 UAE | $59B | 0.8% |
| 24 | 🇦🇺 Australia | $57B | 0.8% |
| 25 | 🇰🇼 Kuwait | $49B | 0.7% |
| 26 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | $48B | 0.7% |
| 27 | 🇮🇱 Israel | $48B | 0.7% |
| 28 | 🇧🇸 Bahamas | $46B | 0.6% |
| 29 | 🇹🇭 Thailand | $46B | 0.6% |
| 30 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | $42B | 0.6% |
| 31 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | $41B | 0.6% |
| 32 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | $40B | 0.5% |
| 33 | 🇮🇹 Italy | $39B | 0.5% |
| 34 | 🇵🇱 Poland | $38B | 0.5% |
| 35 | 🇪🇸 Spain | $37B | 0.5% |
| 36 | 🇻🇳 Vietnam | $37B | 0.5% |
| 37 | 🇨🇱 Chile | $34B | 0.5% |
| 38 | 🇵🇪 Peru | $32B | 0.4% |
| All Other | $439B | 6.0% |
As the above table shows, the United Kingdom is the third highest holder, at over $655 billion in Treasuries. Across Europe, 13 countries are notable holders of these securities, the highest in any region, followed by Asia-Pacific at 11 different holders.
A handful of small nations own a surprising amount of U.S. debt. With a population of 70,000, the Cayman Islands own a towering amount of Treasury bonds to the tune of $284 billion. There are more hedge funds domiciled in the Cayman Islands per capita than any other nation worldwide.
In fact, the four smallest nations in the visualization above—Cayman Islands, Bermuda, Bahamas, and Luxembourg—have a combined population of just 1.2 million people, but own a staggering $741 billion in Treasuries.
Interest Rates and Treasury Market Dynamics
Over 2022, foreign demand for Treasuries sank 6% as higher interest rates and a strong U.S. dollar made owning these bonds less profitable.
This is because rising interest rates on U.S. debt makes the present value of their future income payments lower. Meanwhile, their prices also fall.
As the chart below shows, this drop in demand is a sharp reversal from 2018-2020, when demand jumped as interest rates hovered at historic lows. A similar trend took place in the decade after the 2008-09 financial crisis when U.S. debt holdings effectively tripled from $2 to $6 trillion.
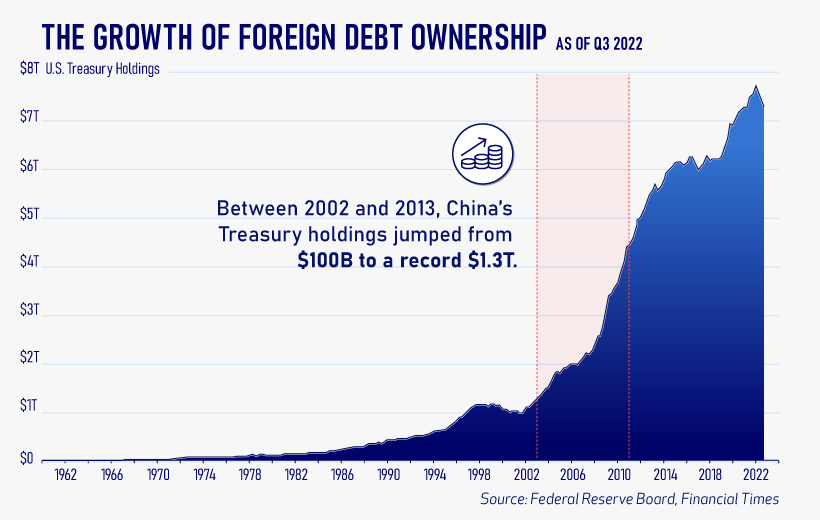
Driving this trend was China’s rapid purchase of Treasuries, which ballooned from $100 billion in 2002 to a peak of $1.3 trillion in 2013. As the country’s exports and output expanded, it sold yuan and bought dollars to help alleviate exchange rate pressure on its currency.
Fast-forward to today, and global interest-rate uncertainty—which in turn can impact national currency valuations and therefore demand for Treasuries—continues to be a factor impacting the future direction of foreign U.S. debt holdings.
Markets
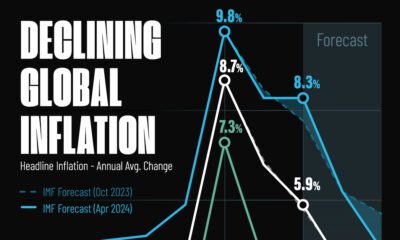
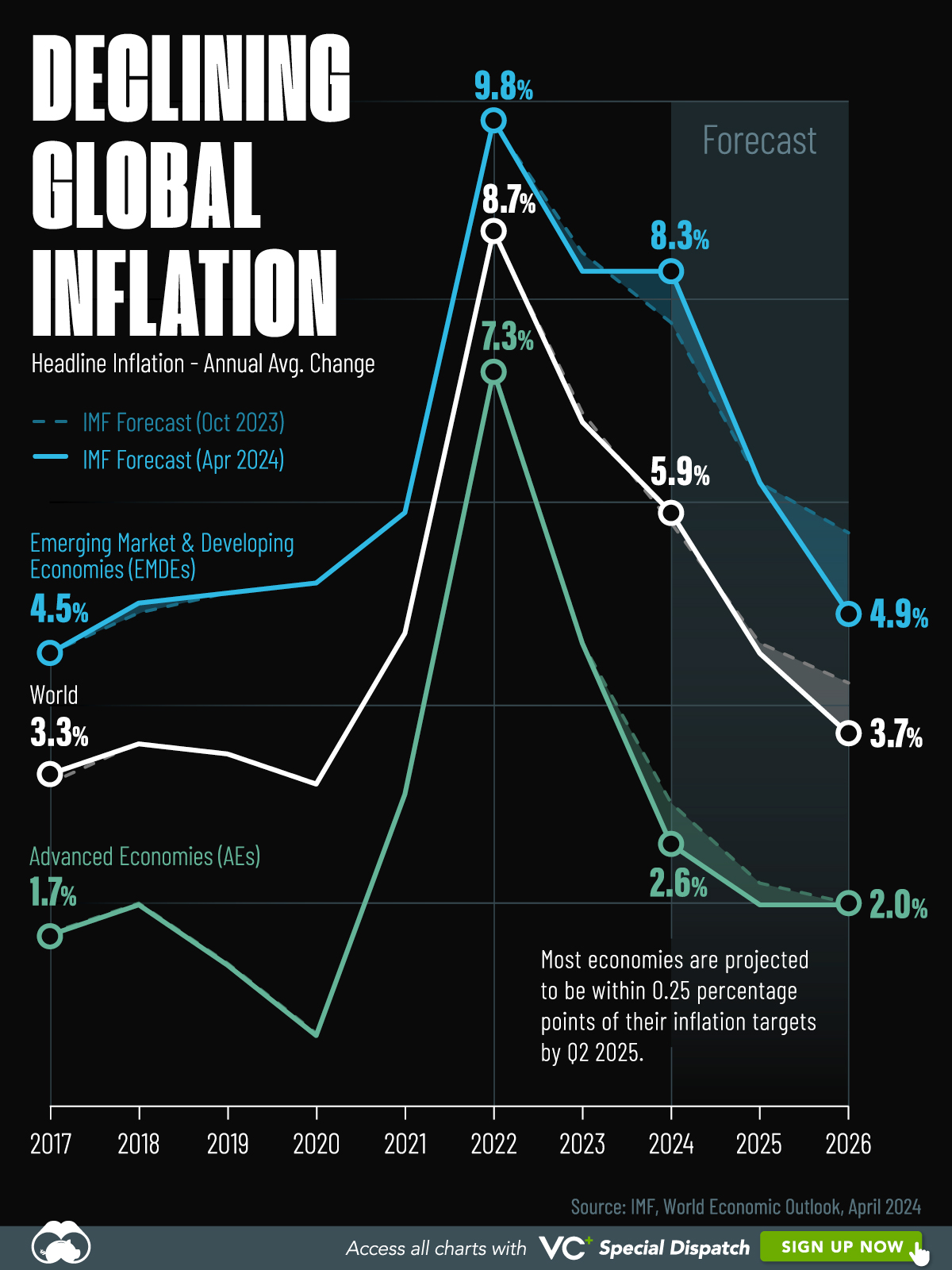
Visualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
Here are IMF forecasts for global inflation rates up to 2026, highlighting a slow descent of price pressures amid resilient global growth.
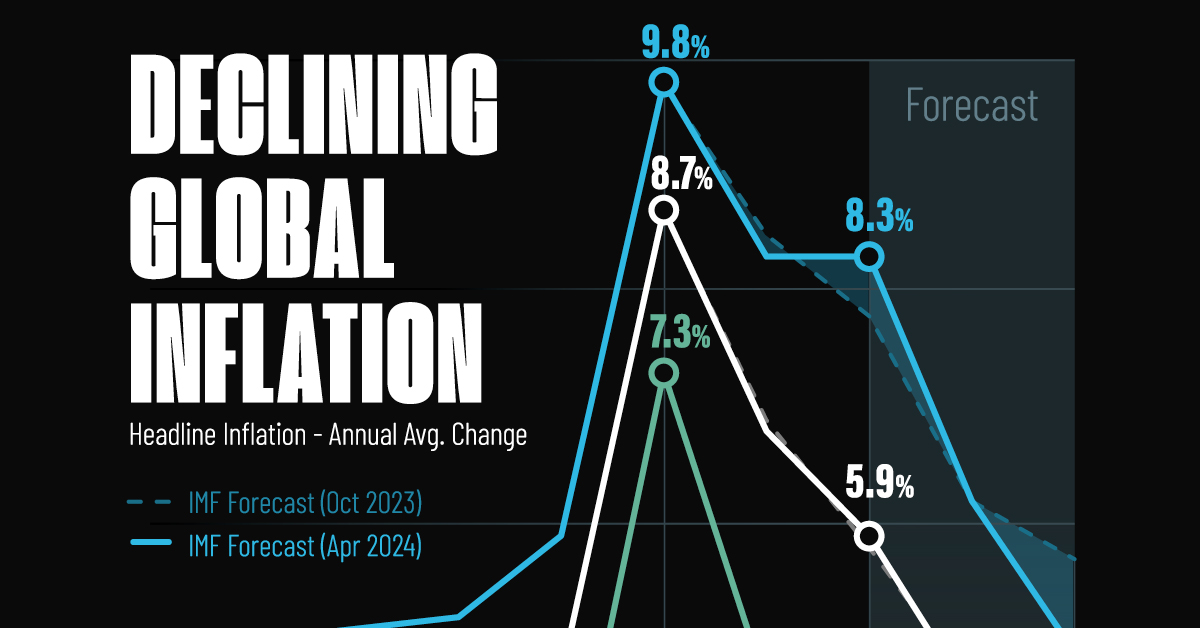
Visualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
Global inflation rates are gradually descending, but progress has been slow.
Today, the big question is if inflation will decline far enough to trigger easing monetary policy. So far, the Federal Reserve has held rates for nine months amid stronger than expected core inflation, which excludes volatile energy and food prices.
Yet looking further ahead, inflation forecasts from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suggest that inflation will decline as price pressures ease, but the path of disinflation is not without its unknown risks.
This graphic shows global inflation forecasts, based on data from the April 2024 IMF World Economic Outlook.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
The IMF’s Inflation Outlook
Below, we show the IMF’s latest projections for global inflation rates through to 2026:
| Year | Global Inflation Rate (%) | Advanced Economies Inflation Rate (%) | Emerging Market and Developing Economies Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 5.1 |
| 2020 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 5.2 |
| 2021 | 4.7 | 3.1 | 5.9 |
| 2022 | 8.7 | 7.3 | 9.8 |
| 2023 | 6.8 | 4.6 | 8.3 |
| 2024 | 5.9 | 2.6 | 8.3 |
| 2025 | 4.5 | 2.0 | 6.2 |
| 2026 | 3.7 | 2.0 | 4.9 |
After hitting a peak of 8.7% in 2022, global inflation is projected to fall to 5.9% in 2024, reflecting promising inflation trends amid resilient global growth.
While inflation has largely declined due to falling energy and goods prices, persistently high services inflation poses challenges to mitigating price pressures. In addition, the IMF highlights the potential risk of an escalating conflict in the Middle East, which could lead to energy price shocks and higher shipping costs.
These developments could negatively affect inflation scenarios and prompt central banks to adopt tighter monetary policies. Overall, by 2026, global inflation is anticipated to decline to 3.7%—still notably above the 2% target set by several major economies.
Adding to this, we can see divergences in the path of inflation between advanced and emerging economies. While affluent nations are forecast to see inflation edge closer to the 2% target by 2026, emerging economies are projected to have inflation rates reach 4.9%—falling closer to their pre-pandemic averages.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets6 days ago
Markets6 days agoThe Best U.S. Companies to Work for According to LinkedIn
-

 VC+2 weeks ago
VC+2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
-

 Wealth1 week ago
Wealth1 week agoCharted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act